Popular Signal Indicators: Your Guide to Trending Tools

When it comes to understanding market movements, signal indicators can be your best friends. These handy tools help you read market trends and make sense of the ups and downs in cryptocurrency. Whether you’re just getting started with trading or have been at it a while, knowing the right indicators can be a game-changer. Some of the most popular indicators, like RSI, MACD, and Bollinger Bands, have been around for ages—and for a good reason. They offer reliable insights and help you make more informed trading decisions.
So, how do these indicators actually work? Let’s break it down in a way that’s easy to digest. From spotting overbought conditions to understanding price trends, these tools are here to keep you updated with what’s trending in the market. And don’t worry—this isn’t a math class! We’ll keep things simple and practical, focusing on how each indicator can boost your trading game.
1. RSI (Relative Strength Index): Spotting Trends with Ease
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a favorite among traders for its ability to reveal market momentum. RSI is a simple, yet powerful, indicator that oscillates between 0 and 100. When the RSI is above 70, it indicates that the asset might be overbought, signaling a potential price drop. When it dips below 30, it’s considered oversold, suggesting a possible upward swing. In simpler terms, RSI helps you understand if a coin is trending up or down too fast, giving you a heads-up for potential reversals.
Imagine you’re keeping an eye on a trending cryptocurrency. With RSI, you can easily see if hype is pushing the price too high or if it’s just the start of a solid trend. It’s like having a little trading compass to navigate market extremes, so you don’t get caught buying at the top or selling at the bottom. Try it out on platforms like TradingView, where you can add RSI to your charts with a single click.
2. MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): Timing Your Entries and Exits
MACD is another popular tool that helps traders understand market trends and momentum. This indicator is all about timing—it helps you spot when trends are likely to start or end. MACD works by showing the relationship between two moving averages: the 26-day and 12-day averages. When these lines cross, it indicates a shift in momentum. A crossover above zero generally suggests a bullish trend, while a cross below zero signals a bearish trend.
If you’re wondering when to jump into a trending coin, MACD can give you an extra layer of insight. For example, a “golden cross” (when the shorter average crosses above the longer one) could hint at a good buying opportunity, while a “death cross” could mean it’s time to consider selling. These signals are particularly useful when the market is trending in a strong direction, as they help you make timely moves without relying solely on gut feeling. You can find the MACD indicator on nearly every trading platform, such as Binance.
3. Bollinger Bands: Keeping Your Trades in Check
Bollinger Bands might sound complicated, but they’re actually pretty straightforward. Created by John Bollinger, this indicator uses three lines: a simple moving average (usually 20 days) and two bands plotted at two standard deviations above and below it. These bands expand and contract with market volatility, which makes them ideal for identifying trending conditions and potential price reversals.
If the price moves toward the upper band, it might mean the asset is overbought, signaling a potential trend change. On the other hand, if the price dips toward the lower band, it could be oversold, indicating a possible bounce back. Bollinger Bands are perfect if you’re looking to understand the “volatility mood” of the market. They’re especially useful in trending markets, helping you decide when to buy or sell within safe boundaries. Experiment with Bollinger Bands on platforms like MetaTrader to see how they fit your trading style.
Combining Indicators for Accuracy: How to Blend Signals Effectively

Relying on one indicator alone is like using a single weather forecast to predict the whole week—you might get lucky, but it’s risky. In trading, blending multiple indicators can give you a more accurate picture of market trends, helping you to spot patterns with greater confidence. Whether you’re just starting or have been trading for a while, combining signals can make your strategy more robust and keep you in tune with what’s trending.
1. Why Combine Indicators? The Power of Confirmation
Using a single indicator might tell you one side of the story, but combining indicators adds a layer of confirmation. Let’s say RSI is telling you that a cryptocurrency is trending as overbought. That’s useful, but how do you know it’s a solid trend and not just a temporary spike? This is where adding MACD or Bollinger Bands can give you more context.
When multiple indicators agree, it’s a stronger signal that a real trend might be in place. For example, if RSI says a coin is overbought and MACD shows upward momentum, this combination provides more assurance that the price is trending up—at least in the short term. Having these combined signals can help you feel more confident in your decisions, knowing that you’re basing them on multiple sources of insight.
2. RSI and MACD: A Perfect Pair for Momentum
A popular pairing for many traders is RSI with MACD. These two indicators focus on momentum but from slightly different angles. RSI (Relative Strength Index) helps you understand whether an asset is overbought or oversold, while MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) provides a clearer picture of the trend’s strength.
Here’s how to blend them: when RSI indicates an overbought condition (above 70), and MACD crosses downward, this can be a double signal that a reversal might be on the way. On the other hand, if RSI is below 30 and MACD crosses upward, it’s a stronger buy signal because both indicators are suggesting an upward trend.
Using these two together can help you avoid jumping in too soon or holding onto a trending asset for too long. If both indicators are flashing the same signal, it’s more likely that the trend is solid. And remember, even though it sounds complex, tools like eToro have easy chart overlays for both RSI and MACD, so you can keep an eye on both indicators without too much hassle.
3. Adding Bollinger Bands for Volatility Insights
Bollinger Bands add another dimension by showing you how volatile the market is. When you combine Bollinger Bands with RSI or MACD, you get a fuller picture of both momentum and volatility—two factors that really matter in trending markets. If an asset’s price reaches the upper Bollinger Band and RSI indicates overbought, it’s often a sign that the price may soon pull back.
Bollinger Bands also help in identifying “breakouts.” If the price suddenly pushes outside of the bands, it could mean a strong trend is forming. Pair this with a MACD upward crossover, and you have a powerful indication that the market is trending in a particular direction. This combo of indicators is especially handy in volatile markets, as Bollinger Bands act like guardrails, helping you spot potential trend reversals before they happen.
Platforms like MetaTrader 4 make it easy to combine Bollinger Bands with other indicators. By overlaying them on one chart, you’ll see when price action aligns with RSI and MACD, giving you more confidence in the signals.
4. Three Tips for Combining Indicators Effectively
Start Simple
Don’t overwhelm yourself by using too many indicators. Choose two or three that align well with your trading style and goals. If you’re just getting started, try sticking with RSI and MACD before adding Bollinger Bands. You’ll gain more clarity and avoid information overload, making it easier to catch the most important trending signals.
Use Indicators for Different Purposes
Each indicator serves a unique function, so pick those that give different types of information. For example, pairing a momentum indicator like RSI with a volatility indicator like Bollinger Bands provides a well-rounded perspective. This blend lets you see if a trend is just getting started or nearing exhaustion.
Adjust Indicators for Different Market Conditions
Markets can shift from trending to range-bound. If the market is trending strongly, RSI and MACD may be your best friends. In choppier conditions, Bollinger Bands can offer insights into volatility shifts. Adapting your combination of indicators based on market conditions will help you make smarter trades and avoid false signals.
5. Practice and Experiment with Demo Accounts
One of the best ways to master combining indicators is through practice. Many platforms, such as CryptoCompare and Binance, offer demo accounts that allow you to test these strategies without risking actual funds. Experiment with different combinations until you find a setup that works best for you and fits your trading style.
When you start seeing trends through the eyes of multiple indicators, you’ll get a clearer picture of what’s truly trending in the market. Remember, trading isn’t about being perfect; it’s about making informed decisions and managing risk.
Identifying Overbought and Oversold Zones: Key Insights for Traders
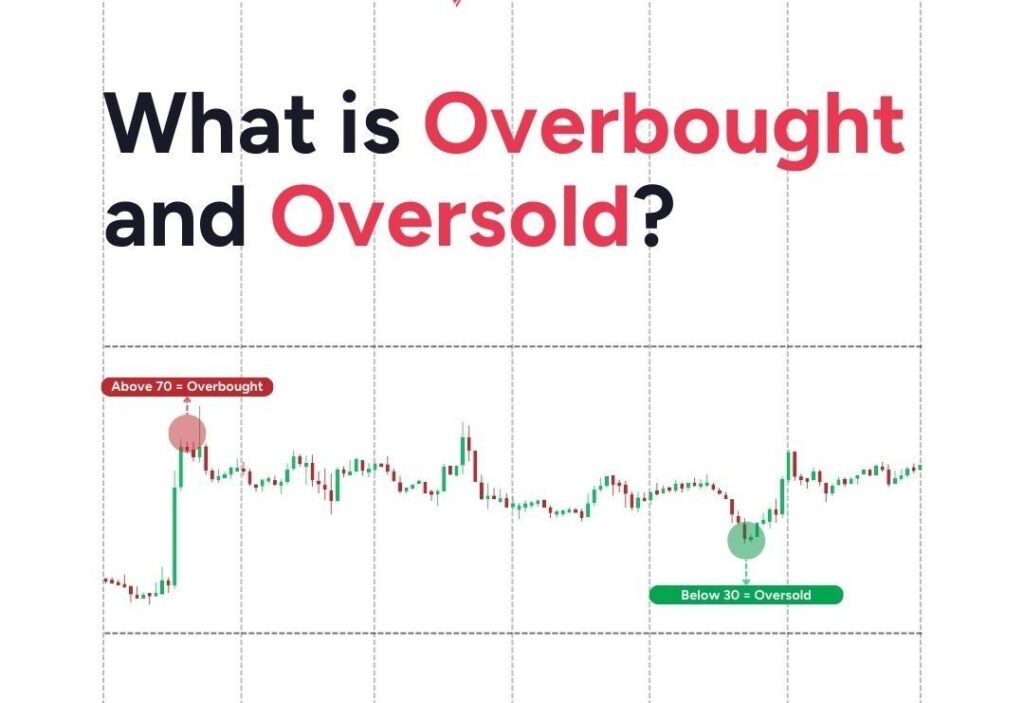
When trading, spotting overbought and oversold zones is like finding shortcuts on a long road. These zones hint at when a trend might be cooling off or heating up, helping you catch moves before they make headlines. Understanding these zones helps you decide whether to stay in, pull out, or jump into a trending trade with confidence. Let’s dive into what these zones are, how to identify them, and the tools that make it easy.
1. Overbought and Oversold: What Does It Mean?
In trading, “overbought” means that a stock or cryptocurrency’s price has risen too quickly. Traders believe it’s due for a drop, as buyers are exhausted. Think of it like everyone’s rushing to grab the latest trending sneakers—eventually, the demand cools off. This can lead to a price correction or even a drop, which may present a selling opportunity.
On the flip side, “oversold” means the price has dropped too much, too fast. Traders think it’s due for a bounce as sellers are exhausted, and buyers may step in. Spotting these zones can help you anticipate possible reversals and avoid getting swept away in a price move that’s about to turn.
Most traders use the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to gauge these zones. The RSI scale ranges from 0 to 100, with values above 70 indicating an overbought condition and values below 30 signaling oversold. You can use popular trading platforms like TradingView to add RSI to your chart and start exploring these zones with ease.
2. Using RSI to Identify Key Zones
RSI, or Relative Strength Index, is one of the most popular tools for identifying overbought and oversold zones. It’s a simple indicator that gives a score from 0 to 100, showing whether the price is trending toward overbought or oversold. When RSI reaches 70 or above, it indicates overbought; when it dips below 30, it signals oversold.
Let’s say you’re watching a trending asset with an RSI of 80. That high RSI might signal it’s overbought, and a reversal could be near. Conversely, if the RSI drops to 25, it’s a sign the asset could be oversold, and a price rally may be around the corner.
This approach isn’t foolproof, but it gives you a starting point. If you’re new to RSI, check out Investopedia’s guide on RSI for a deeper dive. Many traders combine RSI with other indicators, like MACD, to confirm trends and improve their chances of catching profitable moves.
3. Stochastic Oscillator: A Backup for RSI
While RSI is reliable, adding the Stochastic Oscillator to your toolkit can improve accuracy. The Stochastic Oscillator compares the asset’s closing price to its price range over a specific period, usually 14 days. When this oscillator reaches 80, it suggests an overbought trend; when it falls below 20, it indicates oversold.
Imagine watching a trending stock with RSI at 75, signaling it’s close to overbought, and the Stochastic Oscillator shows a reading of 85. This double signal makes it more likely the asset is in overbought territory, possibly ready for a correction. This combination helps filter out false alarms, especially in volatile markets.
Many platforms, including MetaTrader 4, allow you to add multiple indicators to the same chart, so you can easily overlay the Stochastic Oscillator with RSI to see how well they line up.
4. Practical Tips for Using Overbought and Oversold Indicators
Check Trends Before You Act
Always consider the overall trend. In an uptrend, prices may stay overbought longer than expected, and the same goes for oversold zones in a downtrend. Following the trend helps you avoid exiting trades too early.
Combine Indicators for Confirmation
When RSI and the Stochastic Oscillator both signal overbought or oversold, the likelihood of a reversal is stronger. You can experiment with combining RSI and Stochastic on demo platforms like eToro, where you can practice without risk.
Use Support and Resistance Levels
Align RSI or Stochastic signals with support and resistance levels. An overbought RSI near a resistance level is a stronger signal for a pullback, while an oversold RSI near support could indicate a rebound. Adding support and resistance zones to your charts on TradingView is easy and can enhance your analysis.
5. Watching Trends with Real Examples
Let’s say you’re monitoring Bitcoin, a constantly trending asset with frequent price swings. Imagine Bitcoin’s RSI is at 72 and has just hit a long-standing resistance level. This could mean a reversal is imminent, especially if other traders start selling off. In this case, you’d watch closely to see if the price indeed starts to dip, signaling an overbought condition playing out.
On the flip side, if Bitcoin’s RSI is around 28 and nearing a support level, it might be ready for a rebound. This could be an opportunity to buy in before the price rises, especially if other signals confirm the reversal. Real examples help you see these tools in action, so try back-testing on demo accounts or checking out sites like CoinMarketCap for trending assets and their RSI values.
Evaluating Indicator Accuracy: Knowing Which Signals to Trust
Navigating through trading indicators can feel like trying to pick the perfect gift from a shelf full of options. With so many choices, you want to make sure you’re choosing the right signals that offer reliable guidance on the trending moves of the market. Not every indicator is trustworthy in every situation, so knowing which signals to trust can really help you make better decisions.
Let’s break down the ways you can evaluate indicator accuracy, from understanding how different indicators work to combining them for stronger insights.
1. What Makes an Indicator Reliable?
Not all indicators are equally effective for every trading style. Indicators work best when you use them in the right context. For example, trend-following indicators like Moving Averages perform well when the market is trending in a clear direction. But in a choppy, sideways market, these signals may lead to false readings.
Take the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) indicator, a favorite among trend followers. MACD helps you see if the trend is strengthening or fading. When MACD lines cross, it can signal a change in the trend, but this is more useful in trending markets. In ranging markets, the signal may give mixed results.
If you’re new to indicators, checking out Investopedia’s guide on MACD can help you understand how this indicator works. Knowing the conditions where each indicator performs best will help you rely on the right signal at the right time.
2. Cross-Referencing Signals: Don’t Rely on One Alone
Relying on just one indicator is like asking one friend for advice on every decision—it won’t always be right. Combining indicators is a smarter approach. By cross-referencing, you reduce the risk of making decisions based on a single, possibly inaccurate signal.
For example, pairing the Relative Strength Index (RSI) with MACD can give you a clearer picture. When both RSI and MACD confirm the same direction, it’s likely that the trend is genuine. Say RSI indicates an oversold condition (below 30) and MACD shows a bullish crossover. This combined signal is more trustworthy than relying on either indicator alone.
Experiment with this on demo accounts, using tools like MetaTrader 5, where you can see how combining indicators impacts your trading decisions. This will let you experience the power of cross-referencing firsthand and build confidence in your analysis.
3. Evaluating Accuracy with Backtesting
A trending indicator may look great on paper, but how well does it perform in the real market? Backtesting lets you test your indicators against historical data to see if they consistently deliver reliable results. By simulating trades with past data, you can see how often an indicator would’ve led to a profitable decision.
For example, you can take an indicator like Bollinger Bands and test its signals on historical price data. When prices touch the upper or lower bands, it often signals an overbought or oversold condition. But is this pattern accurate for every trending asset? Backtesting will help you answer this.
Platforms like TradingView have built-in backtesting options that allow you to try indicators on past market data. By reviewing the outcomes, you can determine which indicators offer accurate predictions over time, boosting your confidence in their reliability.
4. Looking at Timeframes: Short-Term vs. Long-Term Signals
Some indicators work well in specific timeframes. Short-term signals can be misleading if you’re a long-term investor, and the opposite is true for day traders. So it’s important to match the indicator’s strengths with your preferred trading timeframe.
For instance, moving averages like the 50-day or 200-day MA are excellent for identifying long-term trends. But for day traders, shorter timeframes, such as the 5-minute or 15-minute charts, paired with indicators like Stochastic Oscillators, might be more effective.
Before trusting any signal, consider the timeframe you’re focusing on. You’ll find that some signals make more sense and are more accurate within specific timeframes. Yahoo Finance offers free charting tools where you can switch between timeframes and see how different indicators react, making it easy to evaluate accuracy within your chosen period.
5. Using Tools to Validate Signals
Technology has simplified trading by offering tools that analyze indicator performance for you. Some platforms even have built-in alert systems that notify you when multiple indicators align, which can improve the quality of your trading signals.
Tools like CryptoHopper and CoinMarketCap offer platforms where you can set up alerts for specific indicators. When your chosen indicators align on a trading signal, you’ll get a notification, helping you stay updated without constantly monitoring the charts. This can be incredibly useful in trending markets, where timing is key.
Try setting up alerts for two or more indicators on these platforms to test how often these combined signals lead to profitable trades. It can save you a lot of time and help you trust your trading system.
6. Understanding False Positives: When Indicators Can Mislead
Even the best indicators can give false positives. False signals are especially common in volatile or sideways markets, where price moves erratically. Understanding when to disregard certain signals helps you avoid losses and focus on the most accurate trends.
Let’s say you’re watching Bollinger Bands, a trending indicator that signals overbought or oversold conditions based on price volatility. In a stable trend, Bollinger Bands are reliable, but in a choppy market, prices can touch the bands repeatedly, giving mixed signals. Knowing this helps you decide when it’s worth trusting the indicator.
Reading up on indicator limitations on forums like Reddit’s trading community can provide you with real-world insights from other traders who’ve faced similar challenges. By learning from others’ experiences, you’ll build a better understanding of which signals to rely on and when to disregard them.


